Mouse IL6 / Interleukin-6 Protein
Il-6
- 100ug (NPP1773) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50136-MNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | Il-6 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse IL6 consists of 188 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 21.9 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 22 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 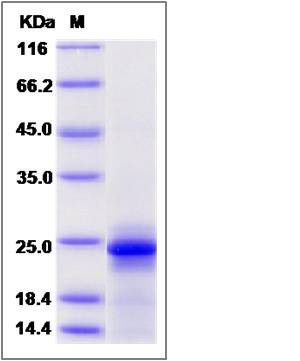 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse IL6 (P08505) (Phe25-Thr211) was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its ability to bind biotinylated rat IL6ST-mFch (P80030-R06H) in a functional ELISA. 2. Measured by its ability to bind biotinylated mouse IL6ST-Fc2h (P50135-M03C) in a functional ELISA. 3. Measured by its ability to bind biotinylated mouse IL6ST-His (P50135-M08H) in a functional ELISA. 4. Measured by its ability to bind biotinylated human IL6RB-Fch (P10974-H03H) in a functional ELISA. 5. Measured in a cell proliferation assay using T1165 mouse plasmacytoma cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.4-2 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Transcription Factor & Regulator |HIF Transcription Factors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a multifunctional α-helical cytokine that regulates cell growth and differentiation of various tissues, which is known particularly for its role in the immune response and acute phase reactions. IL-6 protein is secreted by a variety of cell types including T cells and macrophages as phosphorylated and variably glycosylated molecule. It exerts actions through the its heterodimeric receptor composed of IL-6R that lacks the tyrosine/kinase domain and binds IL-6 with low affinity, and ubiquitously expressed glycoprotein 130 (gp130) that binds the IL-6. IL-6R complex with high affinity and thus transduces signals. IL-6 is also involved in hematopoiesis, bone metabolism, and cancer progression, and has been defined an essential role in directing transition from innate to acquired immunity. |
| Reference |
