Mouse IL7RA / CD127 Protein (His Tag)
CD127,IL-7Ralpha
- 100ug (NPP3202) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50090-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD127,IL-7Ralpha |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse IL7Rα consists of 230 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 26.5 kDa. As a result of different glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rmIL7Rα is approximately 34-40 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 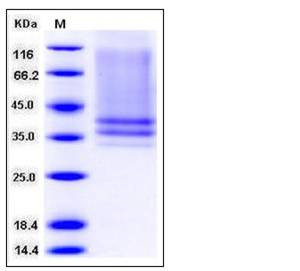 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse IL7Rα (NP_032398.3) extracellular domain (Met 1-Asp 239) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cluster of Differentiation (CD) |T Cell CD Antigen |CD Antigen (Helper T Cells) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interleukin 7 Receptor alpha (IL-7RA), also known as CD127, is a 75 kDa hematopoietin receptor superfamily member that plays an important role in lymphocyte differentiation, proliferation, and survival. IL-7 receptor alpha (CD127) signaling is essential for T-cell development and regulation of naive and memory T-cell homeostasis. IL-7RA is critically required for the proper development and function of lymphoid cells. Therefore, the IL-7RA is critically required for the proper development and function of lymphoid cells. Studies from both pathogenic and controlled HIV infection indicate that the containment of immune activation and preservation of CD127 expression are critical to the stability of CD4(+) T cells in infection. A better understanding of the factors regulating CD127 expression in HIV disease, particularly on T(CM) cells, might unveil new approaches exploiting the IL-7/IL-7R receptor pathway to restore T cell homeostasis and promote immune reconstitution in HIV infection. Factors relevant to HIV infection that could potentially decrease CD127 expression on human CD8(+) T cells. CD127 down-regulation may be an important contributor to HIV-associated T-cell dysfunction. In addition to IL-7, IL-7RA also associates with TSLPR to form the functional receptor for thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) which indirectly regulates T cell development by modulating dendritic cell activation. Mutations in the human IL-7RA gene cause a type of severe combined immunodeficiency in which the major deficiencies are in T cell development, whereas B and NK cells are relatively normal in number. Variation in the IL7RA gene was recently found associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). The polymorphisms in the IL7RA gene is involved in MS pathogenesis and suggest that IL7RA variation may primarily affect chronic disease courses. Soluble CD127 (sCD127) appears to play an important role in the immunopathogenesis of several chronic infections, multiple sclerosis, and various cancers. |
| Reference |
