Mouse ITK Kinase Protein (aa 351-619, His & GST Tag)
Emt,Tcsk,Tsk
- 100ug (NPP3377) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50361-M20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | Emt,Tcsk,Tsk |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse ITK /GST chimera consists of 506 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 58.4 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 58 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 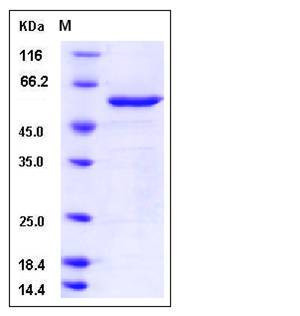 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse ITK / EMT (Q03526) protein kinase domain (Arg 351-Leu 619) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | No Kinase Activity |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Protein Phosphorylation |Tyrosine Kinase |Tec Family |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 7.5, 10% gly, 0.5mM GSH 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | IL-2-inducible T cell kinase is a member of the protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family and TEC subfamily. It contains 1 Btk-type zinc finger, 1 PH domain, 1 protein kinase domain, 1 SH2 domain and 1 SH3 domain. As an intracellular kinase which expressed in T-cells, IL-2-inducible T cell kinase contains both SH2 and SH3 domains which are often found in intracellular kinases. It is hought to play a role in T-cell proliferation and differentiation. It regulates the development, function and differentiation of conventional T-cells and nonconventional NKT-cells. IL-2-inducible T cell kinase also plays an essential role in regulation of the adaptive immune response. efects in IL-2-inducible T cell kinase are the cause of lymphoproliferative syndrome EBV-associated autosomal type 1 (LPSA1). LPSA1 is a rare immunodeficiency characterized by extreme susceptibility to infection with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Inadequate immune response to EBV can have a fatal outcome. Clinical features include splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, recurrent infections. There is an increased risk for lymphoma. |
| Reference |
