Mouse JAM3 / JAM-C Protein (His Tag)
1110002N23Rik,JAM-3,JAM-C,Jcam3
- 100ug (NPP3378) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50465-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 1110002N23Rik,JAM-3,JAM-C,Jcam3 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse JAM3 comprises 221 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 25 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rm JAM3 is approximately 30-35 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Val 32 |
| SDS-PAGE | 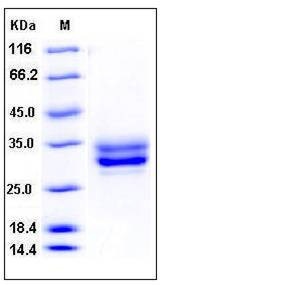 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse JAM3 (NP_075766.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Asn 241) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Cell Adhesion Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris-Citrate, 300mM NaCl, pH 6.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Junctional Adhesion Molecule C Protein & Antibody (JAM-C, JAM3 Protein) also known as Junctional adhesion molecule 3, JAM3, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is an adhesion molecule expressed by endothelial cells (ECs) that plays a role in tight junction formation, leukocyte adhesion, and transendothelial migration. JAM-C is an adhesion molecule that is expressed on cells within the vascular compartment and epithelial cells and, to date, has been largely studied in the context of inflammatory events. JAM-C is also expressed in peripheral nerves and that this expression is localized to Schwann cells at junctions between adjoining myelin end loops. JAM-C is a component of the autotypic junctional attachments of Schwann cells and plays an important role in maintaining the integrity and function of myelinated peripheral nerves. JAM-C was recently shown to be a counter receptor for the leukocyte beta2-integrin Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18), thereby mediating interactions between vascular cells, particularly in inflammatory cell recruitment. JAM-C is up-regulated by oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and may thereby contribute to increased inflammatory cell recruitment during atherosclerosis. JAM-C may therefore provide a novel molecular target for antagonizing interactions between vascular cells in atherosclerosis. JAM-C was shown to undergo a heterophilic interaction with the leukocyte beta2 integrin Mac-1, thereby mediating interactions between vascular cells in inflammatory cell recruitment. JAM-C undergoes a homophilic interaction via the Arg64-Ile65-Glu66 motif on the membrane-distal Ig domain of the molecule. The homophilic interaction of JAM-C can mediate tumor cell-endothelial cell interactions and may thereby be involved in the process of tumor cell metastasis. |
| Reference |
