Mouse LAIR1 Protein (His Tag)
5133400O11Rik,BB115266,D7Bwg0421e,Lair-1
- 100ug (NPP3384) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P51030-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 5133400O11Rik,BB115266,D7Bwg0421e,Lair-1 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse LAIR1 comprises 123 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 14 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 25-35 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 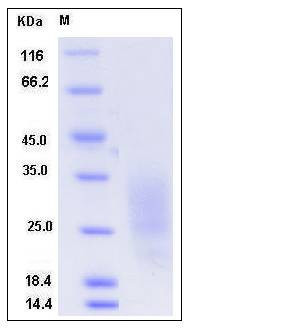 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse LAIR1 (Q8BG84-1) extracellular domain (Gln 22-Ser 133) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cluster of Differentiation (CD) |T Cell CD Antigen |CD Antigen (T Cell Migration/Adhesion) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Leukocyte associated Ig-like receptor-1 (LAIR1) is a surface molecule expressed on human mononuclear leukocytes that functions as an inhibitory receptor on human NK cells. In addition to NK cells, LAIR1 is expressed on T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It is predicted to mediate inhibitory functions based on the presence of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) in its cytoplasmic domain. Cross-linking of LAIR1 on human T cell clones results in inhibition of cytotoxicity only in T cell clones that lack CD28 and are able to spontaneously lyse certain targets in vitro. Moreover, the cytolytic activity of freshly isolated T cells, which is thought to be mainly due to "effector" T cells, can be inhibited by anti-LAIR1 mAb. Thus, LAIR1 functions as an inhibitory receptor not only on NK cells, but also on human T cells. This indicates that LAIR1 provides a mechanism of regulation of effector T cells and may play a role in the inhibition of unwanted bystander responses mediated by Ag-specific T cells. |
| Reference |
