Mouse MCPT1 Protein (His Tag)
AV080368,Mcp-1
- 100ug (NPP3399) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50220-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AV080368,Mcp-1 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse MCPT1 consists of 239 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 26.8 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rm MCPT1 is approximately 32-34 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 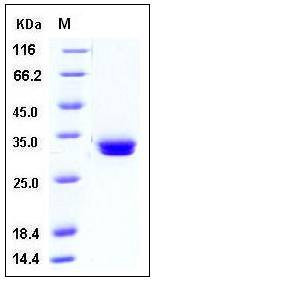 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse MCPT1 (NP_032596.1) (Met 1-Lys 246) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Cells Involved in Inflammation |Mast Cell |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Mouse Mast Cell Protease 1 (MMCP-1), also known as MCP-1, MCPT-1 and β-chymase, is a member of the Chymase family of chymotrypsin-like serine proteases. MCPT-1 is a 26 kDa β-chymase that is a component of mast cell granules. It is a 226 amino acid (aa) protein that has a conserved pattern of six cysteines and one potential glycosylation site. The granule-derived mouse mast cell proteases-1 and -2 (mMCP-1 and -2) colocalize in similar quantities in mucosal mast cells but micrograms of mMCP-1 compared with nanograms of mMCP-2 are detected in peripheral blood during intestinal nematode infection. mMCP-1 isolated from serum is complexed with serpins and both the accumulation and the longevity of mMCP-1 in blood is due to complex formation, protecting it from a pathway that rapidly clears mMCP-2, which is unable to form complexes with serpins. The mucosal mast cell (MMC) granule-specific beta-chymase, mouse mast cell protease-1 (mMCP-1), is released systemically into the bloodstream early in nematode infection before parasite-specific IgE responses develop and TGF-beta1 induces constitutive release of mMCP-1 by homologues of MMC in vitro. Expression of mMCP-1 is largely restricted to intraepithelial MMC and is thought to play a role in the regulation of epithelial permeability. Its activation is completed by the removal of a two residue N-terminal propeptide by a dipeptidyl peptidase (Cathepsin C). MCPT-1 is upregulated in the intestine in response to nematode infection, or in systemic mucosa in response to anaphylaxis. Like human α-chymase, MCPT-1 is capable of the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, which plays a key role in the regulation of arterial pressure. The intestinal inflammation associated with gastrointestinal helminths is partly mediated by mMCP-1. |
| Reference |
