Mouse MERTK / Mer Protein (His & GST Tag)
Eyk,Mer,nmf12,Nyk
- 100ug (NPP3402) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50514-M20B1 |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | Eyk,Mer,nmf12,Nyk |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse MERTK/GST chimera consists of 532 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 61.7 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 58 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 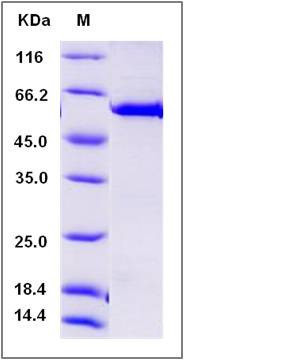 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse MERTK (Q60805) (Glu573-Tyr867) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | The specific activity was determined to be 30 nmol/min/mg using Poly(Glu,Tyr) 4:1 as substrate |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Jak/STAT Signaling |Receptors in the Jak/STAT Pathway |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | &Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase MER (MERTK) is a member of the MER/AXL/TYRO3 receptor kinase family and encodes a transmembrane protein with two fibronectin type-III domains, two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains, and one tyrosine kinase domain. MERTK is localized in membrane and is no expressed in normal B- and T-lymphocytes but is expressed in numerous neoplastic B- and T-cell lines. This protein is highly expressed in testis, ovary, prostate, lung, and kidney, with lower expression in spleen, small intestine, colon, and liver. MERTK regulates many physiological processes including cell survival, migration, differentiation, and phagocytosis of apoptotic cells (efferocytosis). Ligand binding at the cell surface induces autophosphorylation of MERTK on its intracellular domain that provides docking sites for downstream signaling molecules. MERTK signaling plays a role in various processes such as macrophage clearance of apoptotic cells, platelet aggregation, cytoskeleton reorganization and engulfment. MERTK plays also an important role in inhibition of Toll-like receptors (TLRs)-mediated innate immune response by activating STAT1, which selectively induces production of suppressors of cytokine signaling SOCS1 and SOCS3. Defects in MERTK are the cause of retinitis pigmentosa type 38. |
| Reference |
