Mouse Neurexophilin-1 / NXPH1 Protein (His Tag)
C130005L03Rik
- 100ug (NPP2767) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50865-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | C130005L03Rik |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse NXPH1 comprises 261 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 30.1 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 46-48 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ala 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 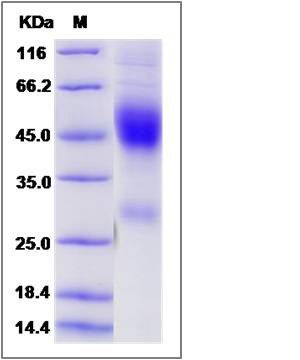 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse NXPH1 (Q61200) (Ala22-Gly271) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Cell Adhesion Proteins |Cytoskeletal Proteins |Regulation |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Neurexophilin-1, or NXPH1 is a secreted glycoprotein, which belongs to the Neurexophilin family. The Neurexophilin family contain at least four genes and resembles a neuropeptide, suggesting a function as an endogenous ligand for alpha-neurexins. The mammalian brains contain four genes for neurexophilins the products of which share a common structure composed of five domains: an N-terminal signal peptide, a variable N-terminal domain, a highly conserved central domain that is N-glycosylated, a short linker region, and a conserved C-terminal domain that is cysteine-rich. Neurexophilin-1 constitutes a secreted cysteine-rich glycoprotein, forms a very tight complex with alpha neurexins, a group of proteins that promote adhesion between dendrites and axons. Neurexophilins 1 and 3 but not 4 (neurexophilin 2 is not expressed in rodents) bind to a single individual LNS domain, the second overall LNS domain in all three alpha-neurexins. |
| Reference |
