Mouse Neuropilin-2 / NRP2 Protein (His Tag)
1110048P06Rik,Np-2,Np2,Npn-2,Npn2
- 100ug (NPP3417) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P57465-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 1110048P06Rik,Np-2,Np2,Npn-2,Npn2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse NRP2 consists of 855 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 96.5 kDa. |
| predicted N | Arg 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 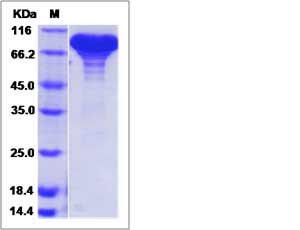 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse NRP2 (NP_001070871.1) (Met1-Pro864) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cytokines & Growth Factors |Growth Factor & Receptor |Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) & Receptor |VEGF Receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Neuropilin-2 (NRP-2) which is related to NRP-1, is a type I? transmembrane glycoprotein and has the structure characteristic with five main extracellular domains: two complement binding (CUB) domains, two coagulation factor V/VIII homology domains, and a MAM (meprin, tyrosine phosphatase domain) region. NRP-2 is a receptor capable of binding two disparate ligands, classⅢ semaphorins (SEMA) and vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF), and thus regulates two diverse systems by activating cellular signaling pathways via interacting with other cell surface receptors such as VEGF receptors and plexins. NRP-2 is well known for its role in facilitating axonal guidance during the development of the neuronal system, and additionally, it is also expressed in vascular endothelial cells and lymphatic endothelium where it affects proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, as well as formation of small lymphatic vessels and capillaries. Recent study has identified NRP-2 as a polysialylated protein expressed in human dendritic cells and modulates DC-T cell Interactions. Nearly all tumor cells express neuropilins and NRP-2 is predominantly expressed in neuronal tumors and melanomas. Furthermore, it is suggested that as the specific ligand for NRP-2, SEMA 3F inhibits tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. |
| Reference |
