Mouse PLA2G7 / PAFAH Protein (His Tag)
R75400
- 100ug (NPP3419) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P51562-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | R75400 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse Pla2g7 consists of 430 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 48.3 kDa. |
| predicted N | Phe 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 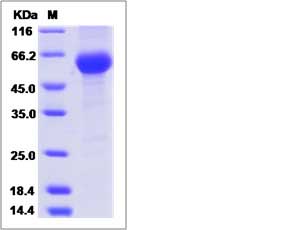 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse Pla2g7 (NP_038765.2) (Met1-Asn440) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Other Signal Transduction Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase, also known as 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase, 2-acetyl-1-alkylglycero-phosphocholine esterase, Group-VIIA phospholipase A2, LDL-associated phospholipase A2, PAF 2-acylhydrolase, PLA2G7 and PAFAH, is secreted protein which belongs to the AB hydrolase superfamily and Lipase family. PLA2G7 / PAFAH modulates the action of platelet-activating factor (PAF) by hydrolyzing the sn-2 ester bond to yield the biologically inactive lyso-PAF. It has a specificity for substrates with a short residue at the sn-2 position. It is inactive against long-chain phospholipids. PLA2G7 / PAFAH is a potent pro- and anti-inflammatory molecule that has been implicated in multiple inflammatory disease processes, including cardiovascular disease. PLA2G7 also represents an important, potentially functional candidate in the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease (CAD). Defects in PLA2G7 are the cause of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase deficiency (PLA2G7 deficiency). It is a trait which is present in 27% of Japanese. It could have a significant physiologic effect in the presence of inflammatory bodily responses. |
| Reference |
