Mouse PLK1 / PLK-1 Protein (His Tag)
Plk,STPK13
- 100ug (NPP3450) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50624-M07B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | Plk,STPK13 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse PLK1 consists of 622 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 70.6 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 65 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 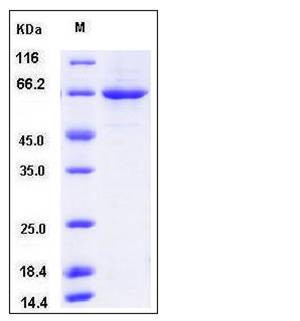 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse PLK1 (Q07832) (Met 1-Ser 603) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | The specific activity was determined to be 3 nmol/min/mg using casein as substrate. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Protein Kinase |Intracellular Kinase |Polo-Like Kinase (PLK) |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Serine / threonine-protein kinase PLK1 / PLK-1, also known as polo-like kinase 1 (PLK-1) or serine / threonine-protein kinase 13 (STPK13), Polo-like kinases (PLKs), is a family of four serine / threonine protein kinases that are critical regulators of cell cycle progression, mitosis, cytokinesis, and the DNA damage response. PLK1 / PLK-1 is ubiquitously expressed. The mRNA and protein expression of PLK1 / PLK-1, -2 and -4 are coordinately regulated during cell cycle progression, but PLK3 levels are independent of the other three family members. PLK1 / PLK-1 is the most well characterized member of this family and strongly promotes the progression of cells through mitosis. During the various stages of mitosis PLK1 / PLK-1 localizes to the centrosomes, kinetochores and central spindle. PLKs are dysregulated in a variety of human cancers. PLK1 / PLK-1 overexpression correlates with cellular proliferation and poor prognosis. Serine / threonine-protein kinase that performs several important functions throughout M phase of the cell cycle, including the regulation of centrosome maturation and spindle assembly, the removal of cohesins from chromosome arms, the inactivation of APC / C inhibitors, and the regulation of mitotic exit and cytokinesis. It is required for recovery after DNA damage checkpoint and entry into mitosis. PLK1 / PLK-1 is required for kinetochore localization of BUB1B, spindle pole localization of isoform 3 of SGOL1 and plays a role in regulating its centriole cohesion function. PLK1 / PLK-1 Phosphorylates BORA, and thereby promotes the degradation of BORA. PLK1 / PLK-1 also contributes to the regulation of AURKA function and phosphorylates SGOL1. |
| Reference |
