Mouse PSMA / FOLH1 Protein (His Tag)
GCP2,mopsm
- 100ug (NPP3325) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50214-M07H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | GCP2,mopsm |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse FOLH1 consists of 725 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 81.8 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 100-110 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 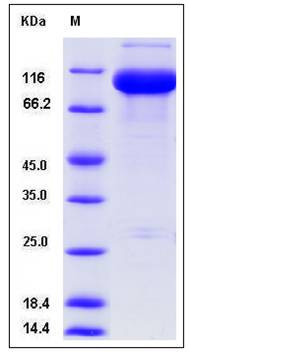 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse FOLH1 (NP_058050.3) extracellular domain (Ile 44-Ala 752) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolic signaling pathways |Amino acid metabolism | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Glutamate carboxypeptidase 2, also known as Glutamate carboxypeptidase II, Membrane glutamate carboxypeptidase, Prostate-specific membrane antigen, GCPII, PSMA, FOLH1, and NAALAD1, is a single-pass type I I membrane protein which belongs to the peptidase M28 family and M28B subfamily. FOLH1 is highly expressed in prostate epithelium. It is detected in urinary bladder, kidney, testis, ovary, fallopian tube, breast, adrenal gland, liver, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, brain (at protein level), and the capillary endothelium of a variety of tumors. FOLH1 has both folate hydrolase and N-acetylated alpha linked acidic dipeptidase (NAALADase) activity. It has a preference for tri-alpha-glutamate peptides. Genetic variation in FOLH1 may be associated with low folate levels and consequent hyperhomocysteinemia. This condition can result in increased risk of cardiovascular disease, neural tube defects, and cognitive deficits. FOLH1 also shows a promising role in directed imaging and therapy of recurrent or metastatic disease. |
| Reference |
