Mouse Periostin / POSTN Protein (His Tag)
A630052E07Rik,AI747096,OSF-2,Osf2,peri,PLF,PN
- 100ug (NPP3442) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50450-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | A630052E07Rik,AI747096,OSF-2,Osf2,peri,PLF,PN |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse POSTN consists of 799 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 89 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rmPOSTN is approximately 80-85 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Asn 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 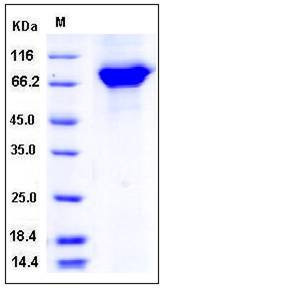 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the full length of mouse POSTN (NP_056599.1) (Met 1-Gln 811) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to induce adhesion of ATDC5 mouse chondrogenic cells. When cells are added to POSTN-His coated plates (10 μg/mL, 100 μL/well), approximately >40% will adhere specifically after 30 minutes at 37℃. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Extracellular Matrix |Structures |Bone | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Periostin ( POSTN ), also known as OSF2 (osteoblast specific factor 2), is a heterofunctional secreted extracellular matrix (ECM) protein comprised of four fasciclin domains that promotes cellular adhesion and movement, as well as collagen fibrillogenesis. Postn is expressed in unique growth centers during embryonic development where it facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of select cell populations undergoing reorganization. In the adult, Postn expression is specifically induced in areas of tissue injury or areas with ongoing cellular re-organization. In the adult heart Postn is induced in the ventricles following myocardial infarction, pressure overload stimulation, or generalized cardiomyopathy. Although the detailed function of Postn is still unclear, Postn-integrin interaction is thought to be involved in tumor development. Postn is frequently overexpressed in various types of human cancers, stimulating metastatic growth by promoting cancer cell survival, invasion and angiogenesis, and can be a useful marker to predict the behavior of cancer. |
| Reference |
