Mouse Pleiotrophin / PTN / HB-GAM Protein
HARP,HB-GAM,HBBN,HBGF-8,HBNF,OSF,Osf-1,Osf1
- 100ug (NPP3449) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P51000-MNAB |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | HARP,HB-GAM,HBBN,HBGF-8,HBNF,OSF,Osf-1,Osf1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse PTN consists of 136 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 15.3 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 20 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gly 33 |
| SDS-PAGE | 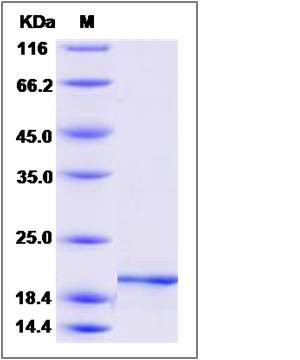 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse PTN (P63089) (Met1-Asp168) was expressed. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized mouse PTN at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind rat SDC1-Fc (P80344-R02H), The EC50 of rat SDC1-Fc (P80344-R02H) is 0.4-1.1 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Hormones |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20 mM Tris, 1M NaCl, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | HB-GAM belongs to the pleiotrophin family. During embryonic and early postnatal development, HB-GAM is expressed in the central and peripheral nervous system and also in several non-neural tissues, notably lung, kidney, gut and bone. While in the adult central nervous system, it is expressed in an activity-dependent manner in the hippocampus where it can suppress long term potentiation induction. HB-GAM has a low expression in other areas of the adult brain, but it can be induced by ischemic insults, or targeted neuronal damaged in the entorhinal cortex or in the substantia nigra pars compacta. It is structurally related to midkine and retinoic acid induced heparin-binding protein and has a high affinity for heparin. HB-GAM binds anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) which induces MAPK pathway activation, an important step in the anti-apoptotic signaling of PTN and regulation of cell proliferation. It also functions as a secreted growth factor and induces neurite outgrowth and which is mitogenic for fibroblasts, epithelial, and endothelial cells. |
| Reference |
