Mouse RCN3 Protein (His Tag)
6030455P07Rik,D530026G20Rik,D7Ertd671e,RLP49
- 100ug (NPP2762) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P51928-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | 6030455P07Rik,D530026G20Rik,D7Ertd671e,RLP49 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse Rcn3 consists of 319 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 36.9 kDa. |
| predicted N | Lys |
| SDS-PAGE | 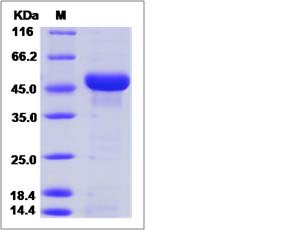 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse Rcn3 (NP_080831.2) (Met1-Leu328) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Signaling Pathway |Calcium Signaling |Calcium Binding Protein |CREC Family | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | RCN3 belongs to the CREC family which contains multiple EF-hand Ca2+-binding proteins localized to the secretory pathway. RCN3 sequence is characterized by the presence of five Arg-Xaa-Xaa-Arg motifs, which represents the target sequence of subtilisin-like proprotein convertases(SPCs). SPCs are a family of seven structurally related serine endoproteases that are involved in the proteolytic activation of proproteins.RCN3 is transiently associated with proPACE4, but not with mature PACE4. Inhibition of PACE4 maturation by a Ca2+ ionophore resulted in accumulation of the proPACE4-RCN-3 complex in cells. It has been proposed that elective and transient association of RCN3 with the precursor of PACE4 plays an important role in the biosynthesis of PACE4. |
| Reference |
