Mouse S100A11 / S100C Protein (His Tag)
cal,Emap1,EMAPI,S100A11,S100a14,S100c
- 100ug (NPP2786) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50227-M07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | cal,Emap1,EMAPI,S100A11,S100a14,S100c |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse S100A11 consists of 114 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 13.2 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 14 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 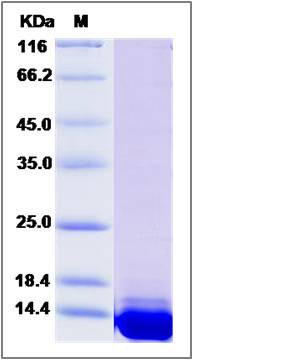 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse S100A11 (NP_058020.1) (Met1-Ile98) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurotransmission |Calcium Signaling |Calcium Binding Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Protein S100-A11, also known as S100 calcium-binding protein A11, S100A11 and MLN70, is a member of the S-100 family. S100A11 is widely expressed in multiple tissues, and is located in cytoplasm, nucleus, and even cell periphery. S100A11 exists as a non-covalent homodimer with an antiparallel conformation. Ca(2+) binding to S100A11 would trigger conformational changes which would expose the hydrophobic cleft of S100A11 and facilitate its interaction with target proteins. As a dual cell growth mediator, S100A11 acts as either a tumor suppressor or promoter in many different types of tumors and would play respective roles in influencing the proliferation of the cancer cells. In the nucleus, S100A11 suppresses the growth of keratinocytes through p21 (CIP1/WAF1) activation and induces cell differentiation. S100A11 is also a novel diagnostic marker in breast carcinoma. |
| Reference |
