Mouse SIRP alpha / CD172a Protein (Fc Tag)
AI835480,Bit,CD172a,P84,Ptpns1,SHP-1,SHPS-1,SIRP
- 100ug (NPP3493) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50956-M02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AI835480,Bit,CD172a,P84,Ptpns1,SHP-1,SHPS-1,SIRP |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse SIRPA/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 583 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 64.9 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rmSIRPA/Fc monomer is approximately 1001-20 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Thr 32 |
| SDS-PAGE | 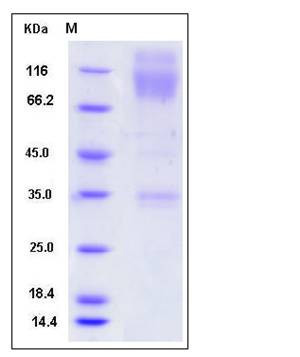 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse SIRPA (BAA20376.1) (Met 1-Asn 373) was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized rat CD47-His (P80305-R08H) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind mouse SIRPA-Fc, The EC50 of mouse SIRPA-Fc is 0.6-1.4 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurology process |Neural Signal Transduction |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type substrate 1, also known as SHP substrate 1, Inhibitory receptor SHPS-1, Brain Ig-like molecule with tyrosine-based activation motifs, Macrophage fusion receptor, CD172 antigen-like family member A, SIRPA and CD172a, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which contains two Ig-like C1-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains and one Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain. SIRPA is ubiquitously expressed. It is highly expressed in brain and detected at lower levels in heart, placenta, lung, testis, ovary, colon, liver, small intestine, prostate, spleen, kidney, skeletal muscle and pancreas. It is also detected on myeloid cells, but not T-cells. SIRPA is an immunoglobulin-like cell surface receptor for CD47. SIRPA acts as docking protein and induces translocation of PTPN6, PTPN11 and other binding partners from the cytosol to the plasma membrane. SIRPA supports adhesion of cerebellar neurons, neurite outgrowth and glial cell attachment. It may play a key role in intracellular signaling during synaptogenesis and in synaptic function. SIRPA is involved in the negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-coupled cellular responses induced by cell adhesion, growth factors or insulin. It mediates negative regulation of phagocytosis, mast cell activation and dendritic cell activation. |
| Reference |
