Mouse SPARCL1 / SPARC-like 1 Protein (His Tag)
Ecm2,hevin,mast9,Sc1
- 100ug (NPP3497) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50544-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Ecm2,hevin,mast9,Sc1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse SPARCL1 comprises 645 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 72.2 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 118 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ile 17 |
| SDS-PAGE | 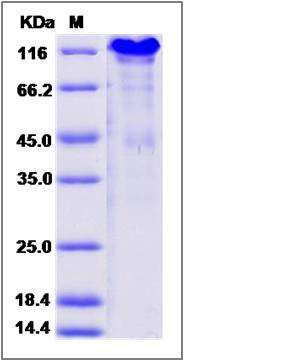 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse SPARCL1 (EDL20231.1) (Met1-Phe650) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Oncoprotein & suppressor & biomarker |Tumor biomarker |Tumor Suppressor |Other in Tumor suppressor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | SPARC-like protein 1 (SPARCL1; also known as SC1, high endothelial venule protein, or hevin) is an extracellular matrix-associated, secreted glycoprotein belonging to the secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) family of matricellular proteins. It contains three conserved structural domains that are implicated in the regulation of cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation. SPARCL1 is expressed during embryogenesis and tissue remodeling and is especially prominent in brain and vasculature. Its down-regulation in a number of cancers and the possibility of its functional compensation by SPARC has led to recent interest in hevin as a tumor suppressor and regulator of angiogenesis. SPARCL1 has antiadhesive properties, and loss of SPARCL1 expression is associated with increased proliferative activity and cell cycle progression. It is suggested that it may influence multiple cellular processes during distinct stages of brain development and function. In addition, SPARCL1 can influence the function of astroglial cells in the developing and mature central nervous system (CNS). |
| Reference |
