Mouse ST6GAL1 / CD75 Protein (His Tag)
AW742324,Siat1,St6gal,St6Gal-I,St6galI
- 100ug (NPP2798) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50740-M07H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AW742324,Siat1,St6gal,St6Gal-I,St6galI |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse ST6GAL1 comprises 396 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 45.9 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of mouse ST6GAL1 is approximately 50-55 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 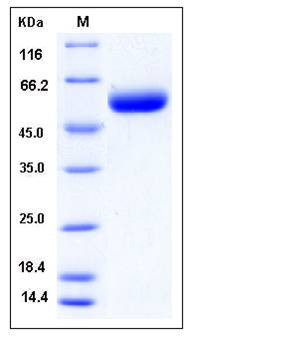 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse ST6GAL1 (NP_666045.1) (Lys 27-Cys 403) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to transfer Neu5Ac from CMP-Neu5Ac to N-Acetyllactosamine. The specific activity is > 150 pmol/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Trafficking |Golgi Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 1, also known as B-cell antigen CD75, Sialyltransferase 1, CMP-N-acetylneuraminate-beta-galactosamide-alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 1, ST6GAL1 and SIAT1, is a single-pass type II membrane protein which belongs to the glycosyltransferase 29 family. Sialyltransferases are key enzymes in the biosynthesis of sialoglycoconjugates that catalyze the transfer of sialic residue from its activated form to an oligosaccharidic acceptor. ST6GAL1 / SIAT1 is normally found in the?Golgi?but which can be proteolytically processed to a soluble form. It is involved in the generation of the cell-surface carbohydrate determinants and differentiation antigens HB-6, CDw75, and CD76. β-Galactoside α2,6-sialyltransferases ST6GAL1 and ST6GAL2 are the two unique members of the ST6GAL family described in higher vertebrates. ST6GAL1 / SIAT1 transfers sialic acid from the donor of substrate CMP-sialic acid to galactose containing acceptor substrates. |
| Reference |
