Mouse SerpinA11 Protein (His Tag)
Gm895
- 100ug (NPP2791) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50435-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Gm895 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse SERPINA11 comprises 414 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 46.2 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rm SERPINA11 is approximately 60-65 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 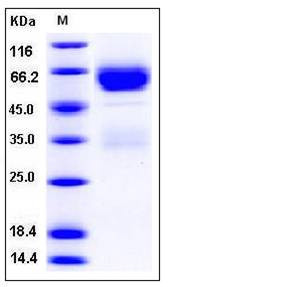 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse SERPINA11 isoform 1 (NP_955018.2) (Met 1-Gly 424) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Plasma Cascade Systems in Inflammation |Fibrinolysis System |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Serpins are the largest and most diverse family of serine protease inhibitors which are involved in a number of fundamental biological processes such as blood coagulation, complement activation, fibrinolysis, angiogenesis, inflammation and tumor suppression and are expressed in a cell-specific manner. Serpins are a group of proteins with similar structures that were first identified as a set of proteins able to inhibit proteases. The acronym serpin was originally coined because many serpins inhibit chymotrypsin-like serine proteases (serine protease inhibitors). Over 1000 serpins have been identified. Mouse Serpin A11, also known as SERPINA11, is a member of the serpin family. |
| Reference |
