Mouse Serum amyloid P component / APCS / SAP Protein (His Tag)
Sap
- 100ug (NPP2795) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50113-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Sap |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse APCS consists of 215 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 25.3 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 28 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 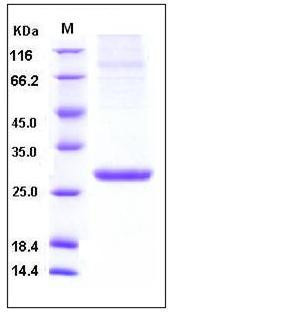 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse APCS (NP_035448.2) (Met 1-Glu 224) precursor was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA . Immobilized mouse APCS at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human Fibronectin Fragment 2 with a linear ranger of 0.625-5 μg/ml . 2. Measured by its ability to bind mouse CD64-AVI in a functional ELISA . |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Acute Phase Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Serum amyloid P component (SAP) is the identical serum form of amyloid P component (AP), a highly preserved plasma protein named for its ubiquitous presence in amyloid deposits. As a normal plasma protein first identified as the pentagonal constituent of in vivo pathological deposits called "amyloid". Serum amyloid P component represents another member of the pentraxin family, a highly conserved group of molecules that may play a role in innate immunity. SAP is a key negative regulator for innate immune responses to DNA and may be partly responsible for the insufficient immune responses after DNA vaccinations in humans. SAP suppression may be a novel strategy for improving efficacy of human DNA vaccines and requires further clinical investigations. |
| Reference |
