Mouse Smad3 Protein (His & GST Tag)
AU022421,Madh3
- 100ug (NPP1682) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50991-M20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | AU022421,Madh3 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse SMAD3/GST chimera consists of 662 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 75.9 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 75 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 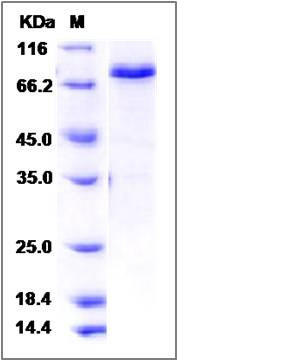 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse SMAD3 (P84025) (Met1-Ser425) was expressed with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Angiogenesis |Cytokine & Receptor |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Superfamily |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Family |TGF-beta Family Modulator | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 2mM GSH, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | SMAD3 belongs to the SMAD family. Members of this family mediate signal transduction by the TGF-beta/activin/BMP-2/4 cytokine superfamily from receptor Ser/Thr protein kinases at the cell surface to the nucleus. SMAD3 is involved in cell signalling. It modulates signals of activin and TGFβ's. Binding of SMAD3 with SMAD4 enables its transmigration into the nucleus where it forms complexes with other proteins and acts as a transcription factor. SMAD3 is a receptor-regulated SMAD (R-SMAD). In mice, mutation of SMAD3 has been linked to colorectal adenocarcinoma, increased systemic inflammation, and accelerated wound healing. Increased SMAD3 activity has been implicated in the pathogenesis of scleroderma. Smad3 is also a multifaceted regulator in adipose physiology and the pathogenesis of obesity and type 2 diabetes. |
| Reference |
