Mouse Syndecan-4 / SDC4 Protein (Fc Tag)
AA959608,AW108331,ryudocan,Synd4,syndecan-4
- 100ug (NPP1595) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50726-M02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AA959608,AW108331,ryudocan,Synd4,syndecan-4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse SDC4/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 364 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 40.5 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 33 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 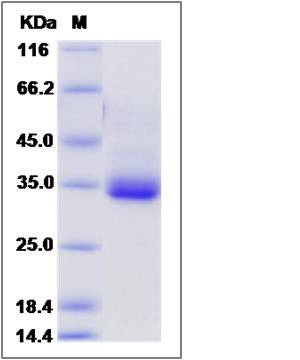 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse SDC4 (O35988)(Met1-Val146) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human MDK (P10247-HNAB) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind mouse SDC4-Fc (P50726-M02H) with a linear range of 0.16-1.25 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Embryogenesis |Axis Formation |Canonical Wnt Pathway |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | SDC4 (Syndecan-4), also known as Syn4, is a transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan that co-operates with integrins during cell-matrix interactions for the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers and in the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) on Tyr397. Syndecan-4 plays roles in the formation of focal adhesions and stress fibers. The cytoplasmic domain of syndecan-4 interacts with a number of signalling and structural proteins, and both extracellular and cytoplasmic domains are necessary for regulated activation of associated transmembrane receptors. Syndecan-4/SDC4 is a heparan sulfate proteoglycan and works as a coreceptor for various growth factors. SDC4 deficiency limits neointimal formation after vascular injury by regulating vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) proliferation and vascular progenitor cells (VPCs) mobilization. Therefore, SDC4 may be a novel therapeutic target for preventing arterial restenosis after angioplasty. |
| Reference |
