Mouse TFPI2 / PP5 Protein (His Tag)
AV000670,PP5/TFPI-2
- 100ug (NPP3503) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P51002-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AV000670,PP5/TFPI-2 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse TFPI2 comprises 200 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 22.8 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 28-32 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Leu 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 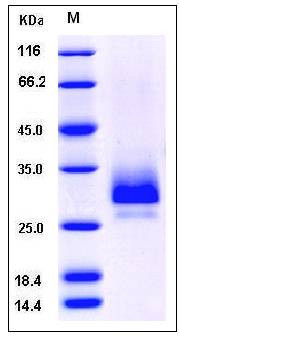 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse TFPI2 (O35536) (Met 1-Lys 211) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Plasma Cascade Systems in Inflammation |Coagulation |Regulatory |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 25mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 (TFPI2), a member of the Kunitz-type serine proteinase inhibitor family, is a structural homologue of tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI). It is a 32 kDa matrix-associated glycoprotein consisting of a short amino-terminal region, three tandem Kunitz-type domains and a positively charged carboxy-terminal tail. TFPI2 inhibits plasmin-dependent activation of several metalloproteinases. TFPI2 is highly abundant in the full-term placenta and widely expressed in various adult human tissues, such as the liver, skeletal muscle, heart, kidney, and pancreas. The expression of TFPI2 in tumors is inversely related to an increasing degree of malignancy, which may suggest a role for TFPI2 in the maintenance of tumor stability and inhibition of the growth of neoplasms. TFPI2 inhibits the tissue factor/factor VIIa (TF/VIIa) complex and a wide variety of serine proteinases including plasmin, plasma kallikrein, factor XIa, trypsin, and chymotrypsin. TFPI2 is involved in regulating pericellular proteases implicated in a variety of physiologic and pathologic processes including cancer cell invasion, vascular inflammation, and atherosclerosis. TFPI2 has also been shown to induce apoptosis and inhibit angiogenesis, which may contribute significantly to tumor growth inhibition. |
| Reference |
