Mouse TIGIT / VSTM3 Protein (His Tag)
ENSMUSG00000071552,Vstm3
- 100ug (NPP3506) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50939-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ENSMUSG00000071552,Vstm3 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse TIGIT comprises 127 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 14.2 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rmSIRPA is approximately 20-25 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gly 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 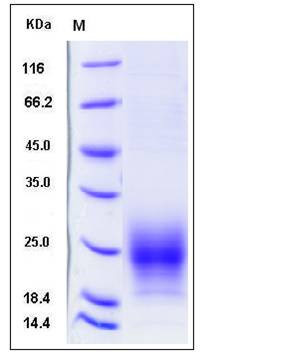 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of mouse TIGIT (NP_001139797.1) (Met 1-Gly 141) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Immobilized mouse TIGIT-His at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind mouse PVR-Fch (P50259-M03H), The EC50 of mouse PVR-Fch (P50259-M03H) is 0.31-0.73 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Adaptive Immunity |T Cell |Non-CD of T cell |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | TIGIT, also known as V-set and transmembrane domain-containing protein 3 (VSTM3) or V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 9 (VSIG9) is a new surface protein containing an immunoglobulin variable domain, a transmembrane domain and an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM). TIGIT is expressed on regulatory, memory, activated T cells and NK cells. It binds PVR with high affinity, and PVRL2 with lower affinity, but not PVRL3. Knockdown of TIGIT with siRNA in human memory T cells did not affect T cell responses, however, TIGIT inhibits NK cytotoxicity directly through its ITIM. TIGIT suppresses T cell activation by promoting the generation of mature immunoregulatory dendritic cells. The binding of PVR to TIGIT on human dendritic cells enhanced the production of IL-10 and diminished the production of IL-12p40. In addition, TIGIT counter inhibits the NK-mediated killing of tumor cells and protects normal cells from NK-mediated cytotoxicity thus providing an "alternative self" mechanism for MHC class I inhibition. |
| Reference |
