Mouse TLR2 Protein (His Tag)
Ly105
- 100ug (NPP3511) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50502-M08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | Ly105 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse TLR2 consists of 573 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 64.8 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 65 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 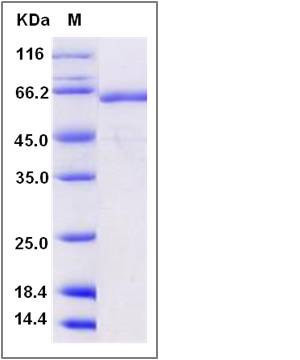 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse TLR2 (Q9QUN7) (Met1-Gln587) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Adapters |Transmembrane |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | TLR2, also known as CD282, is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They play a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. The various TLRs exhibit different patterns of expression. TLR2 contains 14 LRR (leucine-rich) repeats and 1 TIR domain. TLR2 gene is expressed most abundantly in peripheral blood leukocytes, and mediates host response to Gram-positive bacteria and yeast via stimulation of NF-kappaB. CD282 cooperates with LY96 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins and other microbial cell wall components. It also cooperates with TLR1 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins or lipopeptides. CD282 acts via MYD88 and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. It may also promote apoptosis in response to lipoproteins. |
| Reference |
