Mouse TNFRSF19 / TROY Protein (His Tag)
AL023044,AW123854,TAJ,TAJ-ALPHA,TRADE,Troy
- 100ug (NPP3517) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50148-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AL023044,AW123854,TAJ,TAJ-ALPHA,TRADE,Troy |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse TNFRSF19 consists of 152 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 17 kDa. Due to glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rmTNFRSF19 is approximately 25-32 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 30 |
| SDS-PAGE | 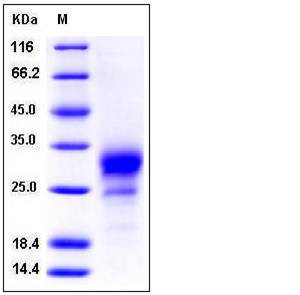 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-Leu 170) of mouse TNFRSF19 (NP_001157627.1) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Angiogenesis |Cytokine & Receptor |Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) & Receptor |TNF Receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 19 (TNFRSF19), also known as TAJ-alpha or TROY, is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. TNFRSF19/TROY expression is detected in the pulmonary epithelium and the ductal epithelium of the prostate and parotid glands. TNFRSF19/TROY expression is detected in some adenocarcinoma cell lines that arise from this tissue. It has been shown to interact with TRAF family members, and to activate JNK signaling pathway when overexpressed in cells. TNFRSF19/TROY is capable of inducing apoptosis by a caspase-independent mechanism, and it is thought to play an essential role in embryonic development. TNFRSF19/TROY was negatively regulated by adipogenic transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBP). TNFRSF19 signals activation of the Jnk pathway and induces cell death. Overexpression of TNFRSF19 also signals NFB activation, comparable and similar to that by p75NGFR. TNFRSF19/TROY is capable of activating key signaling pathways of the TNF receptor family, and its predominant expression patterns suggest that it plays a role in the growth and regulation of epithelial tissues. |
| Reference |
