Mouse TrkA / NTRK1 Protein (His Tag)
C80751,Tkr,trk,TrkA
- 100ug (NPP3525) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P51103-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | C80751,Tkr,trk,TrkA |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant mouse NTRK1 comprises 398 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 43.7 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 69 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ala 34 |
| SDS-PAGE | 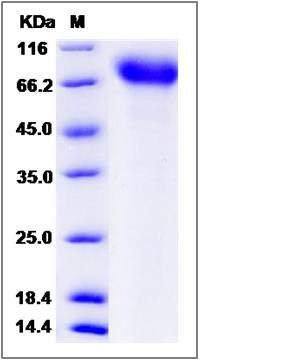 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse NTRK1 (Met1-Gly420) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit NGF-induced proliferation of TF‑1 human erythroleukemic cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.2-1 µg/mL in the presence of 10 ng/mL of recombinant mouse NGF. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | TRKA is a member of the neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor (NTKR) family. It is a membrane-bound receptor that, upon neurotrophin binding, phosphorylates itself and members of the MAPK pathway. Isoform TrkA-III promotes angiogenesis and has oncogenic activity when overexpressed. Isoform TrkA-I is found in most non-neuronal tissues. Isoform TrkA-II is primarily expressed in neuronal cells. TrkA-III is specifically expressed by pluripotent neural stem and neural crest progenitors. The presence of NTRK1 leads to cell differentiation and may play a role in specifying sensory neuron subtypes. Mutations in TRKA gene have been associated with congenital insensitivity to pain, anhidrosis, self-mutilating behavior, mental retardation and cancer. It was originally identified as an oncogene as it is commonly mutated in cancers, particularly colon and thyroid carcinomas. TRKA is required for high-affinity binding to nerve growth factor (NGF), neurotrophin-3 and neurotrophin-4/5 but not brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Known substrates for the Trk receptors are SHC1, PI 3-kinase, and PLC-gamma-1. NTRK1 has a crucial role in the development and function of the nociceptive reception system as well as establishment of thermal regulation via sweating. It also activates ERK1 by either SHC1- or PLC-gamma-1-dependent signaling pathway. Defects in NTRK1 are a cause of congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis and thyroid papillary carcinoma. |
| Reference |
