Mouse VNN1 / Vanin-1 Protein (Fc Tag)
V-1
- 100ug (NPP3539) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50952-M02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | V-1 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse VNN1/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer comprises 705 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 79 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rmVNN1/Fc monomer is approximately 85-90 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Leu 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 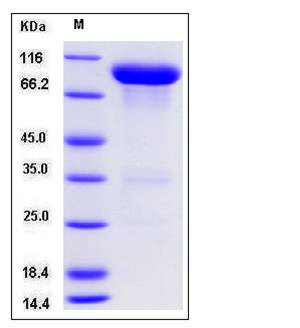 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse VNN1 (Q9Z0K8) (Met 1-Ser 487), without the pro peptide, was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Vitamins / minerals |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Pantetheinase, also known as Pantetheine hydrolase, Vascular non-inflammatory molecule 1, Vanin-1, and VNN1, is a cell membrane protein which belongs to the CN hydrolase family and BTD/VNN subfamily. Vanin-1 contains one CN hydrolase domain. It is widely expressed with higher expression in spleen, kidney and blood. It is overexpressed in lesional psoriatic skin. Vanin-1 is also a member of the Vanin family of proteins which share extensive sequence similarity with each other, and also with biotinidase. The family includes secreted and membrane-associated proteins, a few of which have been reported to participate in hematopoietic cell trafficking. No biotinidase activity has been demonstrated for any of the vanin proteins, however, they possess pantetheinase activity, which may play a role in oxidative-stress response. Vanin-1 is an epithelial pantetheinase that provides cysteamine to tissue and regulates response to stress. Vanin-1 is expressed by enterocytes, and its absence limits intestinal epithelial cell production of proinflammatory signals. Vanin-1 regulates late adhesion steps of thymus homing under physiological, noninflammatory conditions. The early impact of vanin-1 deficiency on tumor induction was directly correlated to the amount of inflammation and subsequent epithelial proliferation rather than cell death rate. Vanin-1 molecule was shown to be involved in the control of thymus reconstitution following sublethal irradiation. |
| Reference |
