Mouse Vitronectin / VTN Protein (His Tag)
AI256434,Vn
- 100ug (NPP3538) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P50585-M08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Mouse |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AI256434,Vn |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant mouse vitronectin consists of 470 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 54.2 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rmvitronectin is approximately 75-85 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Asp 20 |
| SDS-PAGE | 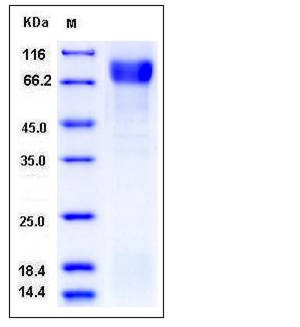 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mouse vitronectin (NP_035837.1) (Met 1-Lys 478) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of DU145 human prostate carcinoma cells. When cells are added to mouse Vitronectin coated plates (10 μg/mL and 100 μL/well), > 60% cells will adhere specifically after 30 minutes at 37 ℃. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Complement System |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Vitronectin, also known as VTN, is a member of the pexin family. It is an abundant glycoprotein found in serum the extracellular matrix and promotes cell adhesion and spreading. Vitronectin is a secreted protein and exists in either a single chain form or a cleaved, two chain form held together by a disulfide bond. Vitronectin is a plasma glycoprotein implicated as a regulator of diverse physiological process, including blood coagulation, fibrinolysis, pericellular proteolysis, complement dependent immune responses, and cell attachment and spreading. Because of its ability to bind platelet glycoproteins and mediate platelet adhesion and aggregation at sites of vascular injury, vitronectin has become an important mediator in the pathogenesis of coronary atherosclerosis. As a multifunctional protein with a multiple binding domain, Vitronectin interacts with a variety of plasma and cell proteins. Vitronectin binds multiple ligands, including the soluble vitronectin receptor. It may be an independent predictor of adverse cardiovascular outcomes following acute stenting. Accordingly, Vitronectin is suggested to be involved in hemostasis, cell migration, as well as tumor malignancy. |
| Reference |
