Rat BAFFR / TNFRSF13C Protein (His Tag)
TNFRSF13C
- 100ug (NPP2977) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80171-R08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | TNFRSF13C |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat TNFRSF13C comprises 73 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 8.3 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 20 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ser 10 |
| SDS-PAGE | 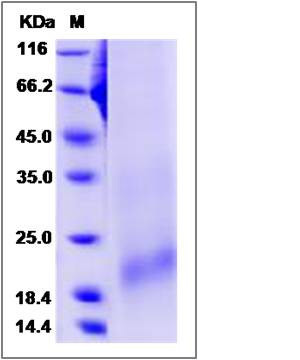 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat TNFRSF13C (D3ZNT3) (Ser10-Ala71) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Cytokines / Chemokines in Angiogenesis |TNF Superfamily |Processes Regulated by TNF Superfamily Members | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 13C (TNFRSF13C) also known as B-cell-activating factor receptor (BAFFR) and CD268 antigen, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. A tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR), or death receptor, is a trimeric cytokine receptor that binds tumor necrosis factors (TNF). The receptor cooperates with an adaptor protein which is important in determining the outcome of the response. Members of the TNF receptor superfamily (TNFRSF) have crucial roles in both innate and adaptive immunity and in cellular apoptosis process. Apoptosis is a cell suicide mechanism that enables metazoans to control cell number in tissues and to eliminate individual cells that threaten the animal's survival. Certain cells have unique sensors, termed death receptors or tumour necrosis factor (TNFR), on their surface. Tumour necrosis factors (TNFR) detect the presence of extracellular death signals and, in response, they rapidly ignite the cell's intrinsic apoptosis machinery. It has been proposed that abnormally high levels of BAFFR/TNFRSF13C (CD268) may contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases by enhancing the survival of autoreactive B cells. |
| Reference |
