Rat CD131 / CSF2RB / IL3RB / IL5RB Protein (Fc Tag)
CSF2Rb, Csf2rb1
- 100ug (NPP3023) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80323-R02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CSF2Rb, Csf2rb1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat CSF2Rb/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 659 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 75.1 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 123 and 89 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 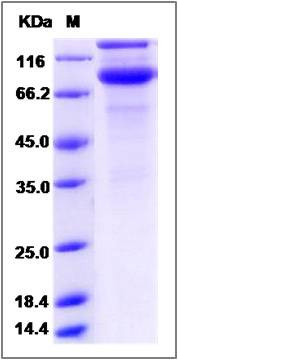 |
| Purity | (24.0+69.6) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat CSF2Rb (Met1-Trp440) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Growth Factor & Receptor |Colony-Stimulating Factor (CSF) & Receptor |CSF Receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Colony stimulating factor 2 receptor, beta, low-affinity (CSF2RB) also known as CD131 antigen (CD131), cytokine receptor common subunit beta, GM-CSF/IL-3/IL-5 receptor common beta-chain, interleukin 3 receptor/granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor 3 receptor, beta (IL3RB), is the common beta chain of the high affinity receptor for IL-3, IL-5 and CSF. Defects in this protein have been reported to be associated with protein alveolar proteinosis (PAP). CD131 belongs to the type I cytokine receptor family. The cluster of differentiation (cluster of designation) (often abbreviated as CD) is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules present on white blood cells initially but found in almost any kind of cell of the body, providing targets for immunophenotyping of cells. Defects in CD131/CSF2RB are the cause of pulmonary surfactant metabolism dysfunction type 5 (SMDP5). SMDP5 is a rare lung disorder due to impaired surfactant homeostasis. It is characterized by alveolar filling with floccular material that stains positive using the periodic acid-Schiff method and is derived from surfactant phospholipids and protein components. Excessive lipoproteins accumulation in the alveoli results in severe respiratory distress. |
| Reference |
