Rat CD89 / FCAR Protein (His Tag)
CD89
- 100ug (NPP3012) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80014-R08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD89 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat FCAR comprises 217 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 24.8 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the rat FCAR is approximately 35-40 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 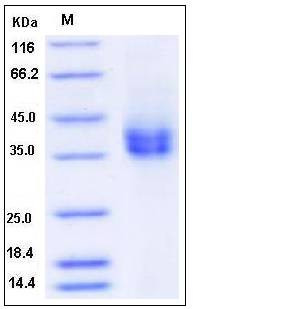 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat FCAR (NP_973721.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Asn 228) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | FCAR, also called FcαRI or CD89, is a type I transmembrane receptor for Fc region of IgA which is the most abundant immunoglobulin in mucosal areas but is only the second most common antibody isotype in serum. This receptor is present on the surface of myeloid lineage cells such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils, especially phagocytes located in mucosal areas. Upon ligand IgA binding, FcαRI associates with the FcR γ signaling molecule bearing the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) through a unique charge-based mechanism and triggers multiple cell-mediated immune responses. It has been reported that Fc RI is a dual-function receptor that can mediate both inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses depending on the type of interaction with its ligand. Sustained aggregation of FCAR results in activation of target-cell functions such as antigen presentation and cytokine release. In contrast, Monomeric targeting with serum IgA or with a variety of anti-FcαRI Fab fragments triggers an inhibitory response and additionally induces apoptosis. FcαRI thus play an fundamental role in preventing tumor development and growth, as well as in controlling inflammation. |
| Reference |
|
