Rat CLEC1A / CLEC-1 Protein (Fc Tag)
CLEC1A
- 100ug (NPP2835) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80212-R01H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CLEC1A |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat CLEC1A comprises 457 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 51.6 kDa. |
| predicted N | Glu |
| SDS-PAGE | 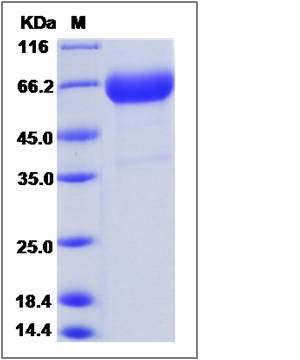 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat CLEC1A (D3ZGU3) (Gln73-Gln269) was expressed, fused with Fc region of human IgG1 at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Lectin |C-tyep lectin | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CLEC1A, also known as CLEC-1, is a member of the C-type lectin/C-type lectin-like domain (CTL/CTLD) superfamily. Members of this family share a common protein fold and have diverse functions, such as cell adhesion, cell-cell signalling, glycoprotein turnover, and roles in inflammation and immune response. CLEC1A contains 1 C-type lectin domain and is expressed preferentially in dendritic cells. It may play a role in regulating dendritic cell function. CLEC1A gene is closely linked to other CTL/CTLD superfamily members on chromosome 12p13 in the natural killer gene complex region. Alternative splice variants have been described but their biological nature has not been determined. CLEC1A is found to be not only expressed in dendritic cells, but also in endothelial cells and in the latter aspect resembles the LOX-1 gene. |
| Reference |
