Rat CLEC4D / CLECSF8 Protein (His Tag)
CLEC4D, Clecsf8, Mcl
- 100ug (NPP2838) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80213-R07H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CLEC4D, Clecsf8, Mcl |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat CLEC4D is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 191 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 22.3 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 29 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 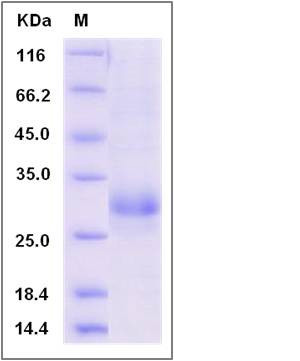 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat CLEC4D (Q69FH1) (Trp48-Lys218) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Lectin |C-tyep lectin | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | C-type lectin (CLEC) family is a type of carbohydrate-binding protein domain named lectin. C-type lectins are the most diverse and prevalent lectin family in immunity with its requirement for calcium for binding. Proteins including a C-type lectin domain have diverse range of functions including cell-cell adhesion, immune response to pathogens and apoptosis. There are at least 14 types of C-type lectins: typeⅠto typeⅩⅣ. CLEC4D(CLECSF8) is a typeⅡ membrane glycoprotein belonging to the C-type lectin family, with restricted expression in the monocyte/macrophage lineage. It plays important roles in the function of macrophages. |
| Reference |
