Rat Coagulation Factor III / Tissue Factor / CD142 Protein (His Tag)
F3
- 100ug (NPP3039) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80407-R08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | F3 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat F3 comprises 235 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 27.2 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 47-52 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ala 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 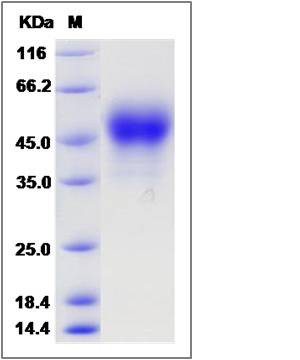 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat F3 (Q66HI4) (Met1-Glu252) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Plasma Cascade Systems in Inflammation |Coagulation |Common |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Tissue factor (TF), also known as coagulation factor III, F3, and CD142, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the tissue factor family. Tissue factor is one of the proteins that participate in hemostatic and inflammatory processes. Activated monocytes present in the liver increase expression of tissue factor, and while accumulating in the organ they can intensify inflammation. Tissue factor is the protein that activates the blood clotting system by binding to, and activating, the plasma serine protease, factor VIIa, following vascular injury. Tissue factor is not only the main physiological initiator of normal blood coagulation, but is also important in the natural history of solid malignancies in that it potentiates metastasis and angiogenesis and mediates outside-in signalling. Tissue factor is expressed constitutively by many tissues which are not in contact with blood and by other cells upon injury or activation; the latter include endothelial cells, tissue macrophages, and peripheral blood monocytes. Coagulation Factor III is a transmembrane glycoprotein that localizes the coagulation serine protease factor VII/VIIa (FVII/VIIa) to the cell surface. The primary function of TF is to activate the clotting cascade. The TF:FVIIa complex also activates cells by cleavage of a G-protein coupled receptor called protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2). TF is expressed by tumor cells and contributes to a variety of pathologic processes, such as thrombosis, metastasis, tumor growth, and tumor angiogenesis. As a key regulator of haemostasis and angiogenesis, it is also involved in the pathology of several diseases, including cardiovascular, inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. |
| Reference |
