Rat DDR1 Kinase / MCK10 / CD167 Protein (His Tag)
DDR1
- 100ug (NPP3024) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80440-R08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | DDR1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat DDR1 comprises 405 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 45.3 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 52 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Asp 20 |
| SDS-PAGE | 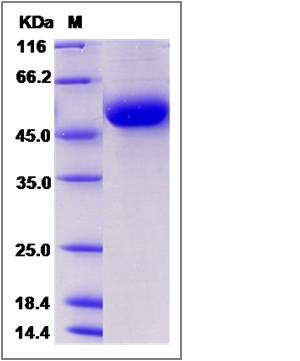 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat DDR1 (Q6MG19) (Met1-Thr413) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Embryogenesis |Germ Layer Formation |Ectoderm Marker |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Discoidin domain receptor family, member 1 (DDR1), also known as or CD167a (cluster of differentiation 167a), and Mammary carcinoma kinase 10 (MCK10), belongs to a subfamily of tyrosine kinase receptors with an extracellular domain homologous to Dictyostellium discoideum protein discoidin 1. Receptor tyrosine kinases play a key role in the communication of cells with their microenvironment. These kinases are involved in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation and metabolism. Expression of DDR1/MCK10/CD167 is restricted to epithelial cells, particularly in the kidney, lung, gastrointestinal tract, and brain. In addition, it has been shown to be significantly overexpressed in several human tumors. DDR1/MCK10/CD167 plays an important role in regulating attachment to collagen, chemotaxis, proliferation, and MMP production in smooth muscle cells. DDR1 functions in a feedforward loop to increase p53 levels and at least some of its effectors. Inhibition of DDR1 function resulted in strikingly increased apoptosis of wild-type p53-containing cells in response to genotoxic stress through a caspase-dependent pathway. |
| Reference |
