Rat EpCAM / TROP-1 / TACSTD1 Protein (His Tag)
EPCAM, Tacstd1
- 100ug (NPP3032) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80306-R08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | EPCAM, Tacstd1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat EPCAM comprises 254 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 29.2 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 39 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 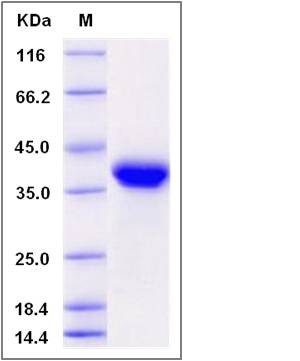 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat EPCAM (O55159) (Met1-Thr266) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cluster of Differentiation (CD) |Other CD Antigen |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule (EpCAM), also known as GA733-2 antigen, is a type â… transmembrane glycoprotein composed of an extracellular domain with two EGF-Like repeats and a cystenin-rich region, a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic domain. It modulates cell adhesion and proliferation. Its overexpression has been detected in many epithelial tumours and has been associated with high stage, high grade and a worse survival in some tumour types. EpCAM has been shown to function as a calcium-independent homophilic cell adhesion molecule that does not exhibit any obvious relationship to the four known cell adhesion molecule superfamilies. However, recent insights have revealed that EpCAM participates in not only cell adhesion, but also in proliferation, migration and differentiation of cells. In addition, recent study revealed that EpCAM is the Wnt-beta-catenin signaling target gene and may be used to facilitate prognosis. It has oncogenic potential and is activated by release of its intracellular domain, which can signal into the cell nucleus by engagement of elements of the wnt pathway. |
| Reference |
