Rat GM-CSF / CSF2 Protein (His Tag)
CSF2, Csfgm
- 100ug (NPP3046) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80020-R07H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CSF2, Csfgm |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat CSF2 comprises 147 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 16.9 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 23 and 20 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 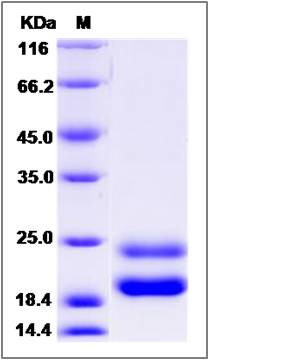 |
| Purity | (32.5+65.6) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat CSF2 (P48750) (Ala18-Lys144) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured in a cell proliferation assay using FDC-P1 cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.02-0.1 ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Monocytes/Macrophages |Macrophage Markers |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is one of an array of cytokines with pivotal roles in embryo implantation and subsequent development. Several cell lineages in the reproductive tract and gestational tissues synthesise GM-CSF under direction by ovarian steroid hormones and signalling agents originating in male seminal fluid and the conceptus. The pre-implantation embryo, invading placental trophoblast cells and the abundant populations of leukocytes controlling maternal immune tolerance are all subject to GM-CSF regulation. GM-CSF stimulates the differentiation of hematopoietic progenitors to monocytes and neutrophils, and reduces the risk for febrile neutropenia in cancer patients. GM-CSF also has been shown to induce the differentiation of myeloid dendritic cells (DCs) that promote the development of T-helper type 1 (cellular) immune responses in cognate T cells. The active form of the protein is found extracellularly as a homodimer, and the encoding gene is localized to a related gene cluster at chromosome region 5q31 which is known to be associated with 5q-syndrome and acute myelogenous leukemia. As a part of the immune/inflammatory cascade, GM-CSF promotes Th1 biased immune response, angiogenesis, allergic inflammation, and the development of autoimmunity, and thus worthy of consideration for therapeutic target. GM-CSF has been utilized in the clinical management of multiple disease processes. Most recently, GM-CSF has been incorporated into the treatment of malignancies as a sole therapy, as well as a vaccine adjuvant. While the benefits of GM-CSF in this arena have been promising, recent reports have suggested the potential for GM-CSF to induce immune suppression and, thus, negatively impact outcomes in the management of cancer patients. GM-CSF deficiency in pregnancy adversely impacts fetal and placental development, as well as progeny viability and growth after birth, highlighting this cytokine as a central maternal determinant of pregnancy outcome with clinical relevance in human fertility. |
| Reference |
