Rat GP1BB / CD42c Protein (Fc Tag)
GP1BB
- 100ug (NPP3049) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80428-R02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | GP1BB |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat GP1BB/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 359 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 40.1 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 63 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Pro 27 |
| SDS-PAGE | 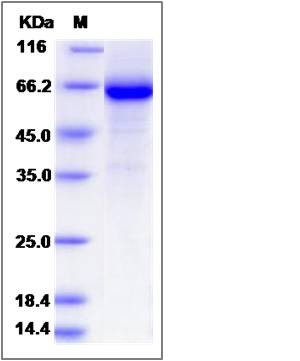 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat GP1BB (Q9JJM7) (Met1-Cys147) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Plasma Cascade Systems in Inflammation |Coagulation |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Platelet glycoprotein Ib (GPIb) complex is best known as a major platelet receptor for von Willebrand factor essential for platelet adhesion under high shear conditions found in arteries and in thrombosis. The GPIb complex is composed of GPIb alpha (Platelet glycoprotein Ib alpha chain) covalently attached to GPIb beta (Platelet glycoprotein Ib beta chain) and noncovalently complexed with GPIX and GPV. GPIb-beta, also known as GP1BB, CD42b-beta and CD42c, is single-pass type I membrane protein expressed in heart and brain, which is a critical component of the von Willebrand factor (vWF) receptor. The cysteine knot region of GPIb beta in the N terminus is critical for the conformation of GPIb beta that interacts with GPIX. The precursor of GP1BB is synthesized from a 1.0 kb mRNA expressed in plateletes and megakaryocytes. GPIb is a heterodimeric transmembrane protein consisting of a disulfide-linked 140 kD alpha chain and 22 kD beta chain. GPIb alpha chain provides the vWF binding site, and GPIb beta chain contributes to surface expression of the receptor and participates in transmembrane signaling through phosphorylation of its intracellular domain. GP1BB is part of the GPIb-V-IX system that constitutes the receptor for von Willebrand factor (vWF), and mediates platelet adhesion in the arterial circulation. Defects in GP1BB are a cause of Bernard-Soulier syndrome (BSS), also known as giant platelet disease (GPD). BSS patients have unusually large platelets and have a clinical bleeding tendency. |
| Reference |
