Rat Growth Hormone Receptor / GHR / GHBP Protein (His Tag)
GHR/BP, MGC124963, MGC156665
- 100ug (NPP3051) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80029-R08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | GHR/BP, MGC124963, MGC156665 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat GHR comprises 258 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 29.6 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the ratGHR is approximately 35-45 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Phe 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 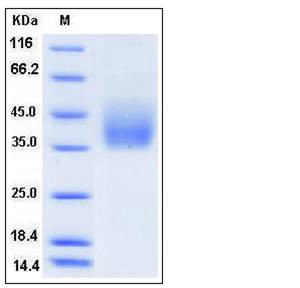 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat GHR (P16310-1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Arg 265) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit proliferation of INS-1 cells induced by human growth hormone. The ED50 for this effect is 0.5-2μg/mL in the presence of 50 ng/mL human growth hormone. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Oncoprotein & suppressor & biomarker |Oncoprotein |Growth Factor & Receptor |Hormones |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Growth hormone receptor, also known as GH receptor and GHR, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the type I cytokine receptor family and type 1 subfamily. GHR contains one fibronectin type-III domain. Growth hormone receptor / GHR is expressed in various tissues with high expression in liver and skeletal muscle. Isoform 4 of GHR is predominantly expressed in kidney, bladder, adrenal gland and brain stem. Isoform 1 expression of GHR in placenta is predominant in chorion and decidua. Isoform 4 is highly expressed in placental villi. Isoform 2 of GHR is expressed in lung, stomach and muscle. Growth hormone receptor / GHR is a receptor for pituitary gland growth hormone. It is involved in regulating postnatal body growth. On ligand binding, it couples to the JAK2 / STAT5 pathway. Isoform 2 of GHR up-regulates the production of GHBP and acts as a negative inhibitor of GH signaling. Defects in GHR are a cause of Laron syndrome (LARS) which is a severe form of growth hormone insensitivity characterized by growth impairment, short stature, dysfunctional growth hormone receptor, and failure to generate insulin-like growth factor I in response to growth hormone. Defects in GHR may also be a cause of idiopathic short stature autosomal (ISSA) which is defined by a subnormal rate of growth. |
| Reference |
