Rat IGFBP6 / IBP6 Protein (His Tag)
Igfbp-6
- 100ug (NPP3113) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P81473-R08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Igfbp-6 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat Igfbp6 consists 212 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 22.9 kDa. |
| predicted N | Ala 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 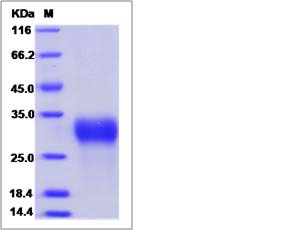 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat Igfbp6 (NP_037236.1) (Met1-Gly226) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Cellular Senescence and Pathways in Aging |Growth Hormone/IGF-I Axis |IGF Family |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 6 (IGFBP6) is a 24-kDa protein that binds insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and IGF-2 with high affinity and inhibits IGF action in vitro. The Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein also known as IGFBP serves as a carrier protein for Insulin-like growth factor 1. IGFBPs are clearly distinct but are sharing regions with strong homology. All members of the IGFBP family bind IGF-I and IGF-II with about equal affinity. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding proteins (IGFBPs) have been shown to either inhibit or enhance the action of IGF, or act in an IGF-independent manner in the prostate. IGF-binding protein-4 (IGFBP-4) inhibits IGF-I action in vitro and is the most abundant IGFBP in the rodent arterial wall. IGFBP6 is directly downregulated by the beta-catenin/TCF complex in desmoid tumors, and imply a role for the IGF axis in the proliferation of desmoid tumors. There is mounting evidence that the structure of the IGFBP proteins plays a key role in the regulation of IGF bioavailability, by modulating its molecular size, capillary membrane permeability, target tissue specificity, cell membrane adherence and IGF affinity. |
| Reference |
