Rat IL1R2 / IL1RB / CD121b Protein (His Tag)
IL1R2
- 100ug (NPP3064) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80196-R08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | IL1R2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat IL1R2 comprises 353 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 39.7 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the rat IL1R2 is approximately 55-60 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Phe 14 |
| SDS-PAGE | 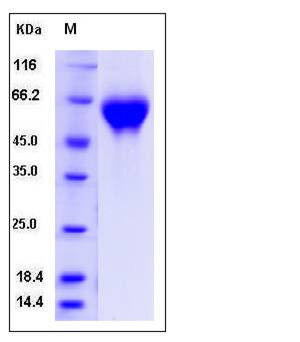 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat IL1R2 (P43303) extracellular domain (Met 1-Glu 355) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to bind biotinylated Rat IL1B-His (P80023-R07E) in a functional ELISA. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Cancer immunology |Cytokine & Receptor |Interleukin & Receptor |IL-1 family & Receptor |IL-1 Family Receptor | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interleukin 1 receptor, type II (IL1R2) also known as CD121b (Cluster of Differentiation 121b) is a cytokine receptor that belongs to the interleukin-1 receptor family. This protein binds interleukin alpha (IL1A), interleukin beta (IL1B), and interleukin 1 receptor, type I (IL1R1/IL1RA), and acts as a decoy receptor that inhibits the activity of its ligands. The pleiotropic cytokine IL1 is produced to regulate development and maintenance of the inflammatory responses, and binds to specific plasma membrane receptors on cells. Two distinct types of IL1 receptors which are able to bind IL1 specifically have been identified, designated as IL1RI (IL1RA) and IL1RII (IL1RB). IL1R1 contributes to IL-1 signaling, whereas the IL-1R2/CD121b has no signaling property and acts as a decoy for IL-1. IL-1R2/CD121b structurally consisting of a ligand binding portion comprised of three Ig-like domains, a single transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic domain, is expressed in a variety of cell types including B lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, large granular leukocytes and endothelial cells. Interleukin 4 (IL4) is reported to antagonize the activity of interleukin 1 by inducing the expression and release of this cytokine. |
| Reference |
