Rat IL23R / IL23 Receptor Protein (Fc Tag)
IL23R
- 100ug (NPP1762) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80395-R02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | IL23R |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat IL23R/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 608 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 69.4 kDa. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 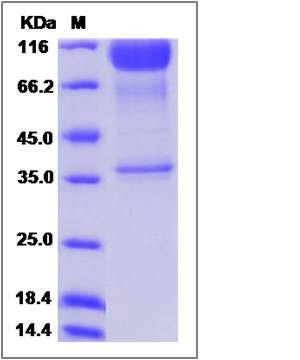 |
| Purity | (75.1+16.6) as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat IL23R (Met1-Asp367) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to bind recombinant mouse IL12Bh (m)+mIL23Ah (PCT028-M08H) in a functional ELISA. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Neuroinflammation |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | IL23R, also known as IL23 receptor, belongs to the type I cytokine receptor family, Type 2 subfamily. It contains 2 fibronectin type-III domains and is expressed by monocytes, Th1, Th0, NK and dendritic cells. Isoform 1 is specifically expressed in NK cells. IL23R associates with IL12RB1 to form the interleukin-23 receptor. It binds IL23 and mediates T-cells, NK cells and possibly certain macrophage/myeloid cells stimulation probably through activation of the Jak-Stat signaling cascade. IL23 functions in innate and adaptive immunity and may participate in acute response to infection in peripheral tissues. IL23 may be responsible for autoimmune inflammatory diseases and be important for tumorigenesis. Genetic variations in IL23R are associated with inflammatory bowel disease type 17 (IBD17). IBD17 is a chronic, relapsing inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract with a complex etiology. Genetic variations in IL23R also can cause susceptibility to psoriasis type 7. |
| Reference |
