Rat KIT / c-KIT Protein (His Tag)
KIT
- 100ug (NPP3076) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80321-R08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | KIT |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat KIT comprises 509 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 56.9 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 83 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ser 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 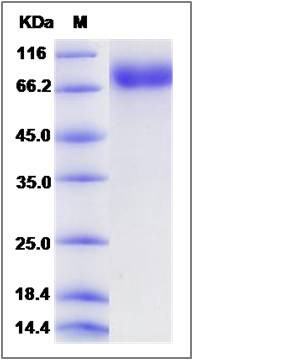 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat KIT (Q63116) (Met1-Thr522) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Protein Kinase |Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | C-Kit is a type 3 transmembrane receptor for MGF (mast cell growth factor, also known as stem cell factor). c-Kit contains 5 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains.and 1 protein kinase domain. It belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, tyr protein kinase family and CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily. C-Kit contains 5 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains and 1 protein kinase domain. C-Kit has a tyrosine-protein kinase activity. Binding of the ligands leads to the autophosphorylation of KIT and its association with substrates such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Antibodies to c-Kit are widely used in immunohistochemistry to help distinguish particular types of tumour in histological tissue sections. It is used primarily in the diagnosis of GISTs. In GISTs, c-Kit staining is typically cytoplasmic, with stronger accentuation along the cell membranes. C-Kit antibodies can also be used in the diagnosis of mast cell tumours and in distinguishing seminomas from embryonal carcinomas. Mutations in c-Kit gene are associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumors, mast cell disease, acute myelogenous lukemia, and piebaldism. Defects in KIT are a cause of acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). AML is a malignant disease in which hematopoietic precursors are arrested in an early stage of development. Note=Somatic mutations that lead to constitutive activation of KIT are detected in AML patients. |
| Reference |
