Rat MBL1 Protein (Fc Tag)
MBL1
- 100ug (NPP3086) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80251-R02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | MBL1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat MBL1/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 462 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 50.5 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 56 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ser 18 |
| SDS-PAGE | 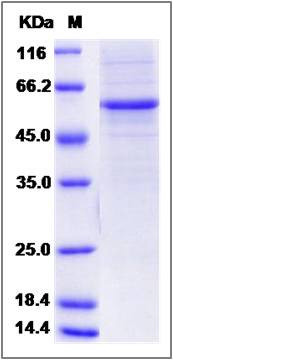 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat MBL1 (P19999) (Met1-Ala238) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Complement System |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Mannose-binding lectin (MBL), also named mannose or mannan-binding protein (MBP), is a C-type lectin which participates in the innate immune system as an activator of the complement system and as opsonin after binding to certain carbohydrate structures on microorganisms and pathogens. Its function appears to be pattern recognition in the first line of defense in the pre-immune host. MBL recognizes carbohydrate patterns found on the surface of a large number of pathogenic micro-organisms including bacteria, viruses, protozoa and fungi. Binding of MBL to a micro-organism results in activation of the lectin pathway of the complement system. Two forms of MBL, MBL-A and MBL-C, were characterized in rodents, rabbits, bovine and rhesus monkeys, whereas only one form was identified in humans, chimpanzees and chickens. The two forms are encoded by two distinct genes named MBL1 and MBL2, which have been identified in many species including the pig. The MBL1 and MBL2 genes encode mannan-binding lectins (MBL) A and C, respectively, that are collagenous lectins (collectins) produced mainly by the liver. The MBL1 gene encodes MBL-A, which has bacteria-binding properties in pigs and rodents but is mutated to a pseudogene in humans and chimpanzees. Deficiency of MBL is probably the most common human immunodeficiency and is associated with an increased risk of mucosally acquired infections including meningococcal disease. MBL could modify disease susceptibility by modulating macrophage interactions with mucosal organisms at the site of initial acquisition. |
| Reference |
