Rat PDGFRa / CD140a Protein (Fc Tag)
PDGFRA
- 100ug (NPP3118) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80433-R02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | PDGFRA |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat PDGFRA/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 741 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 83.2 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 112-120 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Leu 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 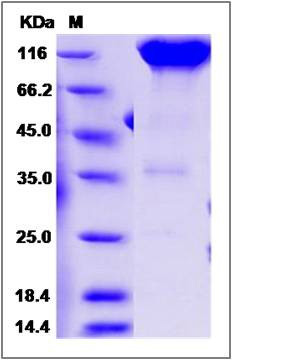 |
| Purity | (96.6+2.8) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat PDGFRA (G3V6A0) (Met1-Glu523) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cytokines & Growth Factors |Growth Factor & Receptor |Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) & Receptor |PDGF Receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | PDGFRA, also known as CD140a, together with the structurally homolog protein PDGFRB (CD140b), are cell surface receptors for members of the platelet-derived growth factor family. They are members of the class III subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTKs) with the similar structure characteristics of five immunoglobulin-like domains in their extracellular region and a split kinase domain in their intracellular region. PDGFRA is expressed in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and mesothelial cell, and binds all three ligand isoforms PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB and PDGF-AB with high affinity, whereas PDGFRB dose not bind PDGF-AA. PDGFRA plays an essential role in regulating proliferation, chemotaxis and migration of mesangial cells. Recent studies have indicated that PDGFRA acts as a critical mediator of signaling in testis organogenesis and Leydig cell differentiation, and in addition, particularly important for kidney development. Additionally, PDGFRA is involved in tumor angiogenesis and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment and has been implicated in development and metastasis of Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). PDGFRA may represent a potential therapeutic target in thymic tumours. PDGFRA gene amplification rather than gene mutation may be the underlying genetic mechanism driving PDGFRA overexpression in a portion of gliomas. |
| Reference |
