Rat REG1A / PSPS Protein (Fc Tag)
Reg,Reg1,REG1A
- 100ug (NPP3123) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80300-R02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Reg,Reg1,REG1A |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat REG1A /Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 319 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 35.8 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 40 and 43 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Leu 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 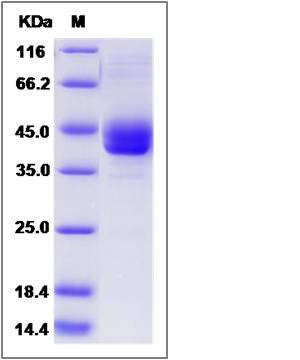 |
| Purity | (55.3+31.4) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat REG1A (P10758) (Met1-Asn100) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Diabetes |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Regenerating (reg) gene encodes protein that has been involved in pancreatic lithogenesis and the regeneration of islet cells and therefore the abnormality of reg genes could be associated with fibrocalculous pancreatopathy. REG I has been shown to be crucial for induction of ductal epithelial cells to differentiate into some cells. Lithostathine-1-alpha, also known as Pancreatic stone protein, Pancreatic thread protein, Regenerating islet-derived protein 1-alpha, REG1A, REG-1-alpha, and PSPS, is highly expressed in fetal and infant brains. REG1A contains one C-type lectin domain and is a known growth factor affecting pancreatic islet beta cells. REG1A may act as an inhibitor of spontaneous calcium carbonate precipitation. It may also be associated with neuronal sprouting in brain, and with brain and pancreas regeneration. REG1A has been reported to be expressed in human cancers, and it may be positively correlated with patient's prognosis. REG3A and REG1A proteins are both involved in liver and pancreatic regeneration and proliferation. High levels of REG1A expression by tumor cells are an independent predictor of a poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). |
| Reference |
