Rat SerpinA1 Protein (His Tag)
SerpinA1
- 100ug (NPP3120) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80476-R08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | SerpinA1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat SERPINA1 consists 398 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 45.2 kDa. |
| predicted N | Glu 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 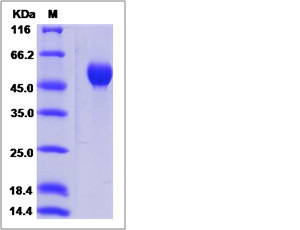 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat SERPINA1 (NP_071964.2) (Met1-Arg411) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Complement and Coagulation |Coagulation |Coagulation Cascade |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | SerpinA1, also known as Alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT), is a prototype member of the Serpin superfamily of the serine protease inhibitors. This serine protease inhibitor blocks the protease, neutrophil elastase. Alpha-1 antitrypsin is mainly produced in the liver and acts as an antiprotease. Its principal function is to inactivate neutrophil elastase, preventing tissue damage. SerpinA1 (alpha1-antitrypsin), an acute phase protein and the classical neutrophil elastase inhibitor, is localized within lipid rafts in primary human monocytes in vitro. It association with monocytes is inhibited by cholesterol depleting/efflux-stimulating agents (nystatin, filipin, MbetaCD (methyl-beta-cyclodextrin) and oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) and conversely, enhanced by free cholesterol. Furthermore, SerpinA1/monocyte association per se depletes lipid raft cholesterol as characterized by the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2, formation of cytosolic lipid droplets, and a complete inhibition of oxLDL uptake by monocytes. Previous population studies have suggested that heterozygote status for the AAT gene (SerpinA1) is a risk factor for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP). Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is a recently identified genetic disease that occurs almost as frequently as cystic fibrosis. It is caused by various mutations in the SerpinA1 gene, and has numerous clinical implications. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is an inherited disease affecting the lung and liver. In the liver, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency may manifest as benign neonatal hepatitis syndrome; a small percentage of adults develop liver fibrosis, with progression to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Its most important physiologic functions are the protection of pulmonary tissue from aggressive proteolytic enzymes and regulation of pulmonary immune processes. |
| Reference |
