Rat TNFR1 / CD120a / TNFRSF1A Protein (His Tag)
TNFRSF1A, Tnfr-1, Tnfr1
- 100ug (NPP3139) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80181-R08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | TNFRSF1A, Tnfr-1, Tnfr1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rat TNFRSF1A comprises 201 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 22.3 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 33-38 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ile 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 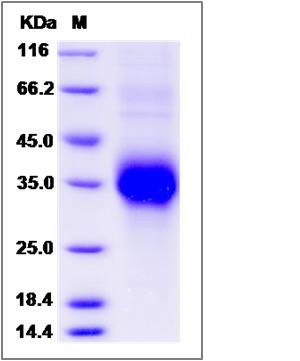 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat TNFRSF1A (Met1-Ala211) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit TNFα-mediated cytotoxicity in L-929 mouse fibroblast cells in the presence of metabolic inhibitor actinomycin D. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.4-2 μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolism processes |Apoptosis |Intracellular | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The cluster of differentiation (CD) system is commonly used as cell markers in immunophynotyping. Different kinds of cells in the immune system can be identified through the surface CD molecules which associating with the immune function of the cell. There are more than 320 CD unique clusters and subclusters have been identified. Some of the CD molecules serve as receptors or ligands important to the cell through initiating a signal cascade which then alter the behavior of the cell. Some CD proteins do not take part in cell signal process but have other functions such as cell adhesion. CD120a (cluste of differentiation 120a), also known as TNFR1 / TNFRSF1A, is a member of CD family, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. CD120a is one of the most primary receptors for the tumor necrosis factor-alpha. It has been shown to be localized to both plasma membrane lipid rafts and the trans golgi complex with the help of the death domain (DD). CD120a can activate the transcription factor NF-κB, mediate apoptosis, and regulate inflammation processes. |
| Reference |
